History
Myall Creek Massacre (1838)
In 1838 white settlers murdered 28 Aboriginal men, women and children near Myall Creek Station. The massacre is a harrowing reminder of Australia's colonial violence and one of the rare cases where killers were tried and hanged.

Wishing you knew more about Aboriginal culture? Search no more.
Get key foundational knowledge about Aboriginal culture in a fun and engaging way.
This is no ordinary resource: It includes a fictional story, quizzes, crosswords and even a treasure hunt.
Stop feeling bad about not knowing. Make it fun to know better.
What happened at Myall Creek?
On 10 June 1838 a group of white settlers murdered 28 Aboriginal men, women and children near Myall Creek Station in northern New South Wales, near Bingara. Seven of the killers were tried and hanged.
The Myall Creek Massacre now serves as both a harrowing reminder of Australia's colonial violence towards Aboriginal people and an example of modern-day reconciliation.
Warning! You might find some of the text here disturbing. It describes strong violence and quotes racist language.
Please also note that this article contains photos of Aboriginal people who have passed.
Historic background
In 1838 white people had settled Australia for just 51 years. Pastoralists were pushing into Aboriginal land, dispossessing Indigenous people from the land that nurtured them physically and spiritually.
Aboriginal people did not give up their land that they had looked after for millennia without a fight. White settlers engaged in many clashes with Aboriginal people at the frontier. Fearing to be outnumbered by Aboriginal tribes some settlers escalated low-level skirmishes to the atrocities we now know as Australia's massacres of Aboriginal people.
With the eyes of the law often several days' ride away the settlers had little to fear. Gangs of stockmen went on what was known as 'the Big Bushwhack' or simply 'the Drive': a hunt for Aboriginal people which lasted several months [1]. They thought there was nothing wrong with shooting Aboriginal people or raping Aboriginal women.
Among the massacres, the one at Myall Creek differs from the many other massacres of Aboriginal people in that it is a well documented and extreme example of what white people were capable of perpetrating on Aboriginal peoples.
Note, however, that the Myall Creek massacre if not famous for what happened to the Aboriginal victims, but for what happened to the white perpetrators.
Myall Creek was the tip of the iceberg of frontier violence against Aboriginal people.
— Prof. Rhonda Craven, Centre for Educational Research, University of Western Sydney [2]
More first Australians were killed than Native Americans on the American frontier and Maoris in New Zealand. The state of Queensland was a slaughterhouse.
— John Pilger, journalist and film-maker [3]
The events of the Myall Creek Massacre on 10 June 1838
Many massacres, including Myall Creek, were witnessed only by the murderers. But because the Myall Creek Massacre has been extensively documented we know now what happened.
At the time about 50 Aboriginal people had moved to Myall Creek Station at the invitation of a stockman employed there.

Ten of them, all able bodied males, were working on a neighbouring station, 50kms away, when they learned that a group of armed stockmen planned to go onto Myall Creek Station. They walked back as fast as they could, but it was already too late.
The stockmen, led by John Fleming, were already galloping towards the huts of Myall Creek Station where the remaining Aboriginal people were preparing their evening meal.
The stockmen herded the defenceless Aboriginal people together and tied their hands together with a long rope. Only two young boys escaped.
The men were deaf to the cries of their victims. Within twenty minutes of their arriving they hauled their captives westwards from the huts and over the top of a rise.
About 800 metres from the huts the defenceless Aboriginal people were hacked and slashed to death. They were beheaded and their headless bodies were left where they fell. The stockmen then set up camp, drinking and bragging about their killings.
Late that night the Aboriginal men who had been working at the neighbouring station arrived at Myall Creek Station. They were urged to move on and headed off into the night.
Two days after the Myall Creek Massacre the murderers returned and burned the bodies of their victims. They then set out to find the ten Aboriginal people they had missed.
They found them the next day and murdered most of them.
Two beautiful young girls were allowed to live so that they could be raped.
— 'Massacre at Myall Creek', The Sydney Morning Herald [4]
It seems likely that the same stockmen perpetrated another massacre near MacIntyre's (near Inverell) where the group of ten Aboriginal people had headed. Reportedly between 30 and 40 Aboriginal people were murdered and their bodies cast onto a large fire.
A woman was allowed to run with blood spurting out of her cut throat. She was then thrown alive onto the fire. Her infant child was thrown alive onto the fire. Two young girls were mutilated by the gang.
Eventually the party immersed into heavy drinking and dispersed five days after their first killings.
Investigating the Myall Creek Massacre
Almost three weeks later the atrocity was reported to police in Sydney in the absence of the local police magistrate. Governor George Gipps ordered an investigation which opened on July 28th, 1838. Eventually ten suspects were identified and marched 300kms to Sydney for trial. Their leader, John Fleming, escaped.
As news spread about the prisoners their capture attracted wide interest. Given the accepted opinion about Aboriginal people of those days the public were soon in favour of the accused and a prominent landholder offered to finance their defence.
I look on the blacks as a set of monkeys, and the earlier they are exterminated from the face of the earth the better... I would never see a white man hanged for killing a black.
— One of the jurors, quoted in The Australian, 18 December 1838 [6]
The first trial in November 1838 was based on thin evidence. No-one apart from the killers had witnessed the massacre and they had removed all bodies before they could be recovered as evidence. The accused pleaded not guilty.
In the absence of any corpse the jury took only 15 minutes to pronounce the accused not guilty to the cheering of the crowd in the court. But Attorney-General James Plunkett asked for and was granted another indictment.
The second trial, ten days later, accused only seven of the original ten men and focused on the killing of just one Aboriginal child. Eventually the jury found them guilty of the murder of the child.
On 18 December 1838 the seven stockmen were hanged. For only the second time in Australian history white men were punished for murder of Aboriginal people [7].
But the NSW governor's commitment to justice for Aboriginal people waned. The involvement of the other three men in the Myall Creek Massacre was never investigated.
The verdict and sentence caused outrage among settlers [1][8]. Petitions were signed and money was raised to employ the best lawyers to defend the murderers [4]. For the murderers it was inconceivable that they had committed a crime given that there had been many such killings. Often the leader of a 'punitive party' and the magistrate responsible for trials were one and the same man [8][2].
Read the protocols of the court proceedings.
The Sydney Morning Herald newspaper was one of the loudest voices in support of the perpetrators. In 2023, on the 185th anniversary of the massacre, they offered their apology.
The whole gang of black animals are not worth the money the colonists will have to pay for printing the silly [court] documents.
— The Sydney Morning Herald, 5 October 1838 [8][6]
Australia on Trial: The Myall Creek Massacre
Homework: Myall Creek is everywhere – even today
In October 2018 a white Chicago police officer was found guilty of second-degree murder. He had shot and killed a black teenager with 16 rounds in 2014.
The teenager was walking "erratically" down a street under the influence of drugs. He was also carrying a small knife.
Those following black deaths in the US called the verdict "historic" because it is so rare that a police officer was held accountable for killing a black person.
Questions
- Find out more about the case. Google "jason van dyke chicago police officer".
- What parallels can you find between the Chicago case and Myall Creek?
- The verdict of the Myall Creek jury caused outrage at the time. What was the reaction to the verdict of the jury in Chicago? With which reaction can you empathise more?
- Why do you think is it so rare that white police is sentenced over black deaths?
After Myall Creek
After the Myall Creek Massacre murderous attacks on Aboriginal people continued for many decades well into the 20th century. White people now went 'underground' using poisoned flour [1] which was harder to prove in court [9]. They also took greater care to conceal or destroy the corpses [9]. Many massacres never became known outside the district where they occurred [8].
One of the last big massacres occurred in 1928 when a group of policemen chained together and shot 50 Aboriginal people in the Northern Territory. Three women were spared to be raped and later burned [10]. It became known as the Coniston Massacre.
Overall, "premeditated butchery of men, women, children and infants accounted in the aggregate for tens of thousands of black lives," reported the Sydney Morning Herald [4], a view Colin Clague confirms. Colin was head of the Aboriginal Land Claims Unit from 1983 to 1988 and vividly remembers the struggle to acknowledge many other massacre sites. Many of them could not be claimed, and when you walk along public reserves or in national parks you might as well come across a massacre site [11].
Myall Creek is all over Australia.
Myall Creek Massacre memorial
Initiatives to erect a memorial on the Myall Creek Massacre site date from as early as 1965. But it wasn't until 1998 that a conference on reconciliation decided to erect a permanent memorial because the participants felt that the 'bad history' had to be acknowledged along with the good. The Myall Creek Memorial Committee was formed to carry out the proposal.
There is a code of silence surrounding the massacres.
— Paulette Smith, Myall Creek Memorial Committee [12]
On 10 June 2000 the Myall Creek Memorial Committee officially opened the Myall Creek Memorial.
The memorial consists of a single, large granite rock. A pathway which leads from the road to the site features seven plaques which briefly explain the history of the massacre. They were made according to artwork by Colin Isaacs.
Travelling to the memorial
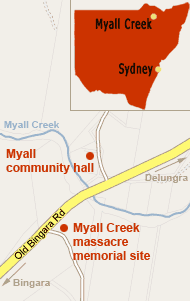
The Myall Creek Massacre memorial is situated in northern NSW between the towns of Bingara and Delungra.
From Sydney travel north to Newcastle then on highway number 15 to Tamworth. Continue north via Manilla and Barraba to Bingara. In Bingara follow the highway number 95 along East St, and after leaving town turn right into Old Bingara Road.
Refer to the map on the right for further details.


Myall Creek Massacre memorial added to national heritage list
On 7 June 2008, 170 years after the Myall Creek Massacre happened, the Federal Heritage Minister Peter Garrett declared the Myall Creek memorial an official national heritage site. Myall Creek joins as the 79th place to be included on the national heritage list which protects natural, historic and Indigenous places of outstanding heritage value to the nation.
The protection the Myall Creek Massacre memorial enjoys through its listed heritage status is welcome because the memorial was damaged in 2005 when vandals hammered words out of some plaques [13].
The events at Myall Creek resonate across the years and the listing of the Myall Creek Massacre and Memorial Site formally recognises a pivotal moment in Australia's history.
— Peter Garrett, Federal Heritage Minister [14]

On 14 November, 2010 the site was given the state's highest form of heritage protection and recognition when Minister for Planning, Tony Kelly, announced it was listed on the State Heritage Register because it represents an important part of the history of New South Wales.
Myall Creek Massacre memorial—
a reconciliation site
With all the violence and atrocities associated with Myall Creek it is hard to imagine that the memorial is also a place of reconciliation.
Ever since the 1980s, annual commemorations recalled the events and remembered both the murderers and the victims of the massacre at Myall Creek.
In 1998 Sue Blacklock, a descendant of an Aboriginal survivor, approached the Rev. John Brown to offer Myall Creek as a reconciliation project. [8]
Coincidentally Beulah Adams, a woman descended from one of those hanged, and Des Blake, descendant of another murderer, also came forward.
Sue acknowledged the courage of Beulah and Des and all felt a strong connection between them. Des told his story in schools—any Australian with ancestors of the 'pioneering days' could have similar links to atrocities in the past.
By their coming together these people make Myall Creek an outstanding example of history used to reconcile and restore relationships. Sue, Beulah and Des still meet during the annual commemorations at the Myall Creek memorial site.
Throughout the 1950s and 1960s I used to think, 'If they could do [the killings] then, they still might'. Deep down I sometimes still think that way... It's sometimes hard to lose the young girl inside.
— Sue Blacklock [15]

Video: Reconciling Murder
What would you do if your ancestors were responsible for one of the country's worst Aboriginal massacres? Meet the family confronting its history head on.
Resources

Roger Milliss' Waterloo Creek: The Australia Day Massacre of 1838 describes the Australia Day 1838 Waterloo Creek and Myall Creek massacres of Aboriginal people.
It is easy to read and keeps you horrified and glued to it at the same time. Milliss was the co-winner of the National Book Council's 1992 Banjo Award. 'Waterloo Creek' includes a detailed reference with many endnotes and pages of bibliography.
This book inspired the group Kilminister to write a song about the Myall Creek Massacre (see below).

Demons at Dusk by Peter Stewart describes the Myall Creek Massacre in a half-novel, half-historic manner.
I can't put this book down. As an Australian I am appalled that not only did the massacre happen but also that this wasn't an isolated incident.
— 'browneyedgirl' in an ABC reader forum

Blood on the Wattle by Bruce Elder informs about massacres and maltreatment of Aboriginal people. It was voted one of the most influential works of Australian non-fiction by newspaper readers in the 'Spectrum Poll of the Century'.
Make sure to pick up the third edition which includes a new chapter on the massacres in the New England area of NSW and around the Three Rivers - the Hastings, the Macleay and the Manning (120 kms north-east of Newcastle).

Craig Lahiff's movie Black and White is about an Aboriginal man who is falsely accused to have murdered a nine-year-old white girl.
The movie documents how white people, police, judges, townsfolk, have no doubt of the Aboriginal man's guilt and what a white lawyer can lose when he sets out to defend the accused.
ABC1 documented the Myall Creek Massacre trials in the 3rd part of their "Australia On Trial" mini-series in April 2012.
Resources on massacres in Victoria: Gippsland Massacres - The Destruction Of The Kurnai tribe, 1800-1860, Peter Gardner and Scars in the landscape: A register of massacre sites in western Victoria, 1803-1859, Ian Clark.
The Wikipedia provides a list of massacres of Indigenous peoples in Australia.
Two good websites you can check out are the Sydney Friends of Myall Creek and the Australian Frontier Conflicts.
Songs about the Myall Creek Massacre
"Kilminister's Confession" by Kilminister
In 2007 the group Kilminister recorded the song Kilminister's Confession which tells the thoughts of one of the white men, Charlie Kilminister, who murdered the Aboriginal people at Myall Creek.
Laurie McGinness from Kilminister says [16]: "The Kilminister character is an amalgamation of several of those involved so the song should not be considered as a completely accurate recount of the events... I changed the story for dramatic effect and to emphasise the cycle of violence, abuse breeds abuse, so the brutalisation of the convicts flowed into the brutalisation of the Indigenous people."
Lyrics: Kilminister's Confession
My name is Charlie Kilminister and tomorrow I must die When the sun comes up I will stand upon the scaffold high With six of my companions beneath the crowd's gaze At the end of a rope, short and strong, I will end my days Jack Ketch will be the hangman and he'll hang us true and well When the sun goes down tomorrow, we'll be on pour way to hell God doesn't care for murderers or so the priest did say But if I go to hell I don't care, I already spent ten years there I was sent to the colony of New South Wales for stealing a pound, a pound of nails They took me from my wife and child, it's the things a man loses that drive him wild Out beyond the Big River, to Myall Creek I was delivered In the heart of an Aboriginal nation well beyond the limits of location My master was Henry Dangar and I was his convict fool I've known a lot of evil men but never one so cruel He had me march to Patrick Plains for twice times fifty on my back Then the bastard turned me round and marched me straight back Most of the blacks were dead already from the work of Cobban and Nunn The few that were left hid in the bush and from the stockmen they did run Some women and kids and a few old men took shelter at our station They were about ail that was left of a great Aboriginal nation There was a woman named Ippeta who with her husband I did share She felt the scars upon my back, I thought she cared though her skin was black Well Daddy was an old man and Billy but a boy Somehow into our misery they brought a little joy John Russell was a stockman who hated all the blacks With George Cobban he had ridden on many great bushwhacks He heard about the group we had at Myall Creek like Satan he did tempt me, like Judas I was weak We took them out and murdered them, for no reason that I know And when it came to Ippeta, I killed her with one blow The power of pure evil was strong upon my mind But still I cannot understand how I was so blind The night is nearly over and the sun will surely rise Soon it will be time to die with those I do despise But one question still haunts me won't you tell me if you can Why Major Nunn, who did worse than me, will never hang and still is free My name is Charlie Kilminister and tomorrow I must die When the sun comes up I will stand upon the scaffold high With six of my companions beneath the crowd's gaze At the end of a rope, short and strong, I will end my days
Lyrics published with kind permission by Laurie McGinness from Kilminister. The CD features another song about a massacre, called Waterloo Creek. Download a sampler of the song 'Kilminister' (mp3, 1.2MB; published with permission).
"John Fleming" by Timeline
Timeline recorded a song based on the Myall Creek Massacre called John Fleming (the leader of the stockmen) which can be heard in full on Timeline's website.
"Near Myall Creek" by George Huitker and Junk Sculpture
George Huitker and his band Junk Sculpture released a song called "Near Myall Creek" hoping to raise further awareness of this history, particularly of injustice and trans-generational trauma.
Plays about the Myall Creek massacre
Maurice Strandgard wrote a play titled Massacre which was published in 1991. It was performed at the Castlemaine Fringe Festival in Castlemaine, Victoria.
And John Summons was equally inspired to write Massacre at Myall Creek, published in 1993.